RFS (simply the abbreviation for Responsive Font Size) is a font size engine which automatically calculates the appropriate font size based on the dimensions of the browser viewport. It's available in one of your favourite preprocessors or postprocessor: Sass, Less, Stylus or PostCSS.
# RFS [![npm][npm-image]][npm-url] [![licence][licence-image]][license-url] [![build][build-image]][build-url] - [How does it work?](#how-does-it-work) - [Installation](#installation) - [Usage](#usage) - [Visualisation](#visualisation) - [Configuration](#configuration) - [`!important` usage](#important-usage) - [Demos](#demos) - [Creator](#creator) - [Copyright and license](#copyright-and-license) ## How does it work? - Font sizes will **rescale for every screen or device**, this prevents long words from being chopped off the viewport on small devices - RFS will prevent the font size from rescaling too small so readability can be assured - **Super easy** to use, just use the `font-size` mixin (or `responsive-font-size` property for PostCSS) instead of the `font-size` property - The font sizes of all text elements will always remain in relation with each other 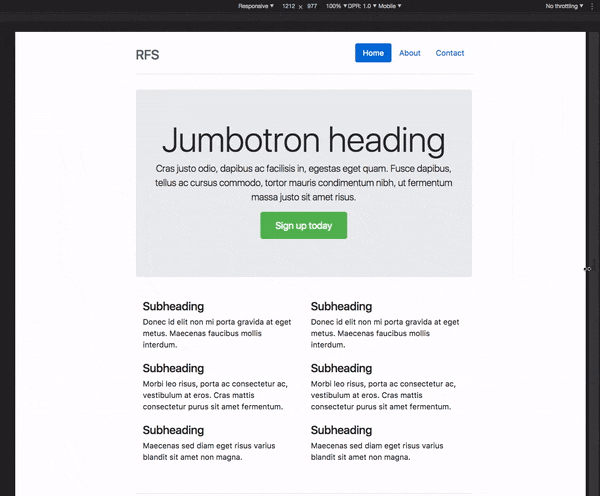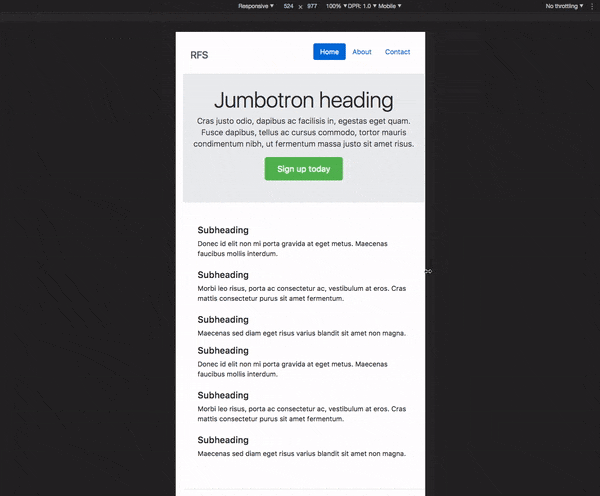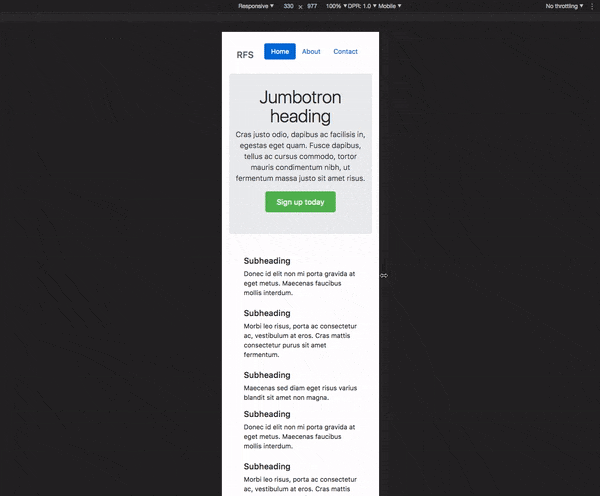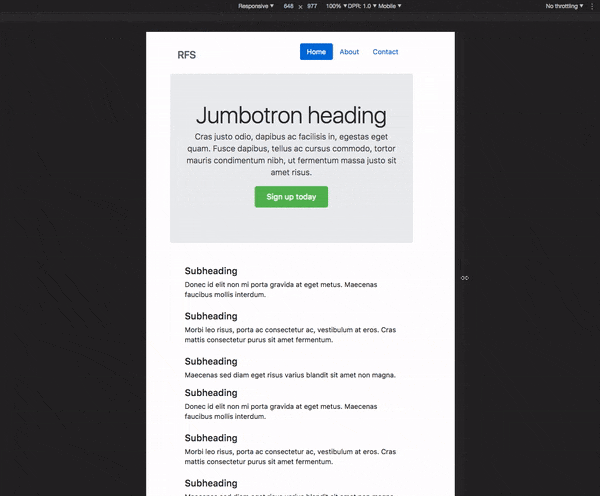 ## Installation RFS can be installed using a package manager (recommended): - npm: `npm install rfs` - yarn: `yarn add rfs` - bower (deprecated): `bower install rfs --save` **Copy/paste (not recommended):** The source files can also be downloaded manually and used in a project. This method is not recommended because you lose the ability to easily and quickly manage and update RFS as a dependency. ## Usage In the following examples, this folder structure is assumed (you will probably just use one pre/postprocessor): ```text project/ ├── postcss/ │ └── main.css ├── less/ │ └── main.less ├── node_modules/ │ └── rfs │ └── ... ├── sass/ │ └── main.sass ├── scss/ │ └── main.scss └── stylus/ └── main.styl ``` ### Sass `.scss` syntax: ```scss // scss/main.scss @import "../node_modules/rfs/scss"; .title { @include font-size(4rem); // or @include responsive-font-size(64px); // or @include rfs(64); } ``` `.sass` syntax: ```sass // scss/main.scss @import "../node_modules/rfs/sass" .title +font-size(4rem) // or +responsive-font-size(64px) // or +rfs(64) ``` ### PostCSS ```postcss // postcss/main.css .title { responsive-font-size: 4rem; // or rfs: 64; } // Handle postcss afterwards (see examples folder for PostCSS example) ``` ### Less ```less // less/main.less @import "../node_modules/rfs/less"; .title { .font-size(4rem); // or .responsive-font-size(64px); // or .rfs(64); } ``` ### Stylus ```stylus // stylus/main.styl @import "../node_modules/rfs/stylus"; .title responsive-font-size(64px) // or rfs(64) ``` Note the `font-size` mixin can not be used to set the font size. That is because a `font-size()` mixin would override the `font-size` property. See [129#issuecomment-477926416](https://github.com/twbs/rfs/pull/129#issuecomment-477926416) for more info. ### Generated css ```css .title { font-size: 4rem; } @media (max-width: 1200px) { .title { font-size: calc(1.525rem + 3.3vw); } } ``` If you're using Webpack, you can simplify the `@import` using the `~` prefix: ```scss @import "~rfs/scss"; ``` ```sass @import "~rfs/sass" ``` ```less @import "~rfs/less"; ``` ```stylus @import "~rfs/stylus" ``` ## Visualisation If you wonder how the font sizes are rescaled, wonder no more and stare at this graph which might clarify things a bit:  Each color represents another font size being rescaled. For example: ```scss .title { @include font-size(40px); } ``` This is the green line. A font size of `40px` stays `40px` in viewports with a size larger than `1200px`. Below `1200px`, the font size is rescaled and at viewport of `360px`, the font size is about `27px`. Note that every font size is generated in a combination of `rem` and `vw` units, but they are mapped to `px` in the graph to make it easier to understand. ## Configuration RFS works out of the box without any configuration tweaks, but if you feel the urge to go loco and fine tune the way font sizes are rescaled, you can: ### Base font size (unit in `px` or `rem`) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-base-font-size` - Less: `@rfs-base-font-size` - PostCSS: `baseFontSize` The option will prevent the font size from becoming too small on smaller screens. If the font size which is passed to RFS is smaller than this base font size, no fluid font rescaling will take place. *Default value: `1.25rem`* ### Font size unit (`px` or `rem`) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-font-size-unit` - Less: `@rfs-font-size-unit` - PostCSS: `fontSizeUnit` The output font size will be rendered in this unit. Setting it in `px` will disable the ability for users to change the the font size in their browser. *Default value: `rem`* ### Breakpoint (in `px`, `em` or `rem`) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-breakpoint` - Less: `@rfs-breakpoint` - PostCSS: `breakpoint` Above this breakpoint, the font size will be equal to the font size you passed to RFS; below the breakpoint, the font size will dynamically scale. *Default value: `1200px`* ### Breakpoint unit (`px`, `em` or `rem`) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-breakpoint-unit` - Less: `@rfs-breakpoint-unit` - PostCSS: `breakpointUnit` The width of the max width in the media query will be rendered in this unit. *Default value: `px`* ### Factor (number) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-factor` - Less: `@rfs-factor` - PostCSS: `factor` This value determines the strength of font size resizing. The higher the factor, the less difference there is between font sizes on small screens. The lower the factor, the less influence RFS has, which results in bigger font sizes for small screens. The factor must me greater than 1. *Default value: `10`* ### Rem value (number) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-rem-value` - Less: `@rfs-rem-value` - PostCSS: `remValue` The value of `1rem` in `px`. The value of `1rem` is typically `16px` but if the font size is changed for `html` the value of `1rem` changes. This variable can be used to change the default value but be careful with it because changing it could lead to unexpected behaviour, for example if additional CSS is loaded which expects `1rem` to be `16px`. *Default value: `16`* ### Two dimensional (boolean) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-two-dimensional` - Less: `@rfs-two-dimensional` - PostCSS: `twoDimensional` Enabling the two dimensional media queries will determine the font size based on the smallest side of the screen with `vmin`. This prevents the font size from changing if the device toggles between portrait and landscape mode. *Default value: `false`* ### Class (boolean) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-class` - Less: `@rfs-class` - PostCSS: `class` RFS can be enabled or disabled with a class. There are 3 options: - `false` No extra classes are generated. - `disable` When the the disable classes are generated you can add the `.disable-responsive-font-size` class to an element to disable responsive font sizes for the element and its child elements. - `enable` RFS is disabled by default in this case. The `.enable-responsive-font-size` class can be added to an element to enable responsive font sizes for the element and its child elements. *Default value: `false`* ### Safari iframe resize bug fix (boolean) - SCSS, Sass & Stylus: `$rfs-safari-iframe-resize-bug-fix` - Less: `@rfs-safari-iframe-resize-bug-fix` - PostCSS: `safariIframeResizeBugFix` Safari doesn't resize its font size in an iframe if the iframe is resized. To fix this `min-width: 0vw` can be added and that's what happens if this option is enabled. See [#14](https://github.com/twbs/rfs/issues/14). *Default value: `false`* ## !important usage By setting a second parameter to true, `!important` is added after the font-size value. (Example is in `scss`) ```scss .label { @include responsive-font-size(2.5rem, true); } ``` CSS: ```css .label { font-size: 2.5rem !important; } @media (max-width: 1200px) { .label { font-size: calc(1.375rem + 1.5vw) !important; } } ``` ## Best practices - Don't set RFS on the `html` element, because this influences the value of `rem` and could lead to unexpected results. - Always set your line-heights relative (in `em` or unitless) to prevent interline issues. ## Browser support RFS is supported by all browsers that support [media queries](https://caniuse.com/#feat=css-mediaqueries) and [viewport units](https://caniuse.com/#feat=viewport-units). In browsers like IE8 or older, the font size will be set but the fluid rescaling will be disabled. A list of the most popular browsers that support RFS: - Chrome - Safari - Opera - Firefox - Edge - Samsung Internet - UC Browsers - IE >= 9 ## Demos - [Simple Codepen Demo](https://codepen.io/MartijnCuppens/pen/ZBjdMy) - [RFS in Bootstrap demo](https://project-rfs.github.io/) ## Creator **Martijn Cuppens** -