1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
|
# 
**Quick Links**:
[**Roadmap**][roadmap] |
[Want to Contribute?](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/issues?scope=all&utf8=%E2%9C%93&state=opened&label_name[]=Accepting%20merge%20requests) |
[GitLab Gitaly Issues](https://gitlab.com/groups/gitlab-org/-/issues?scope=all&state=opened&utf8=%E2%9C%93&label_name%5B%5D=Gitaly) |
[GitLab Gitaly Merge Requests](https://gitlab.com/groups/gitlab-org/-/merge_requests?label_name%5B%5D=Gitaly) |
--------------------------------------------
Gitaly is a Git [RPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_procedure_call)
service for handling all the git calls made by GitLab.
To see where it fits in please look at [GitLab's architecture](https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/development/architecture.html#system-layout).
## Project Goals
Fault-tolerant horizontal scaling of Git storage in GitLab, and particularly, on [gitlab.com](https://gitlab.com).
This will be achieved by focusing on two areas (in this order):
1. **Migrate from repository access via NFS to gitaly-proto, GitLab's new Git RPC protocol**
1. **Evolve from large Gitaly servers managed as "pets" to smaller Gitaly servers that are "cattle"**
## Current Status
As of GitLab 11.5, almost all application code accesses Git repositories
through Gitaly instead of direct disk access. GitLab.com production no
longer uses direct disk access to touch Git repositories; the [NFS
mounts have been
removed](https://about.gitlab.com/2018/09/12/the-road-to-gitaly-1-0/).
For performance reasons some RPCs can be performed through NFS still. An
effort is made to mitigate performance issues by removing [Gitaly N+1](https://gitlab.com/groups/gitlab-org/-/epics/827).
Once that is no longer necessary we can conclude the migration project by
[removing the Git repository storage paths from gitlab-rails's
configuration](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/issues/1282).
In the meantime we are building features according to our [roadmap][roadmap].
If you're interested in seeing how well Gitaly is performing on
GitLab.com, read about our [observability story](doc/observability.md)!
##### Overall

[Dashboard](https://dashboards.gitlab.net/d/gitaly-main/gitaly-overview)
##### By Feature

[Dashboard](https://dashboards.gitlab.net/d/000000198/gitaly-features-overview?orgId=1)
## Installation
Most users won't install Gitaly on its own. It is already included in
[your GitLab installation](https://about.gitlab.com/install/).
Gitaly requires Go 1.16 or Go 1.17 and Ruby 2.7. Run `make` to download and
compile Ruby dependencies, and to compile the Gitaly Go executable.
Gitaly uses `git`. Versions `2.33.0` and newer are supported.
## Configuration
The administration and reference guide is [documented in the GitLab project](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/gitaly/).
## Contributing
See [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md).
## Name
Gitaly is a tribute to git and the town of [Aly](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aly). Where the town of
Aly has zero inhabitants most of the year we would like to reduce the number of
disk operations to zero for most actions. It doesn't hurt that it sounds like
Italy, the capital of which is [the destination of all roads](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/All_roads_lead_to_Rome). All git actions in
GitLab end up in Gitaly.
## Design
High-level architecture overview:
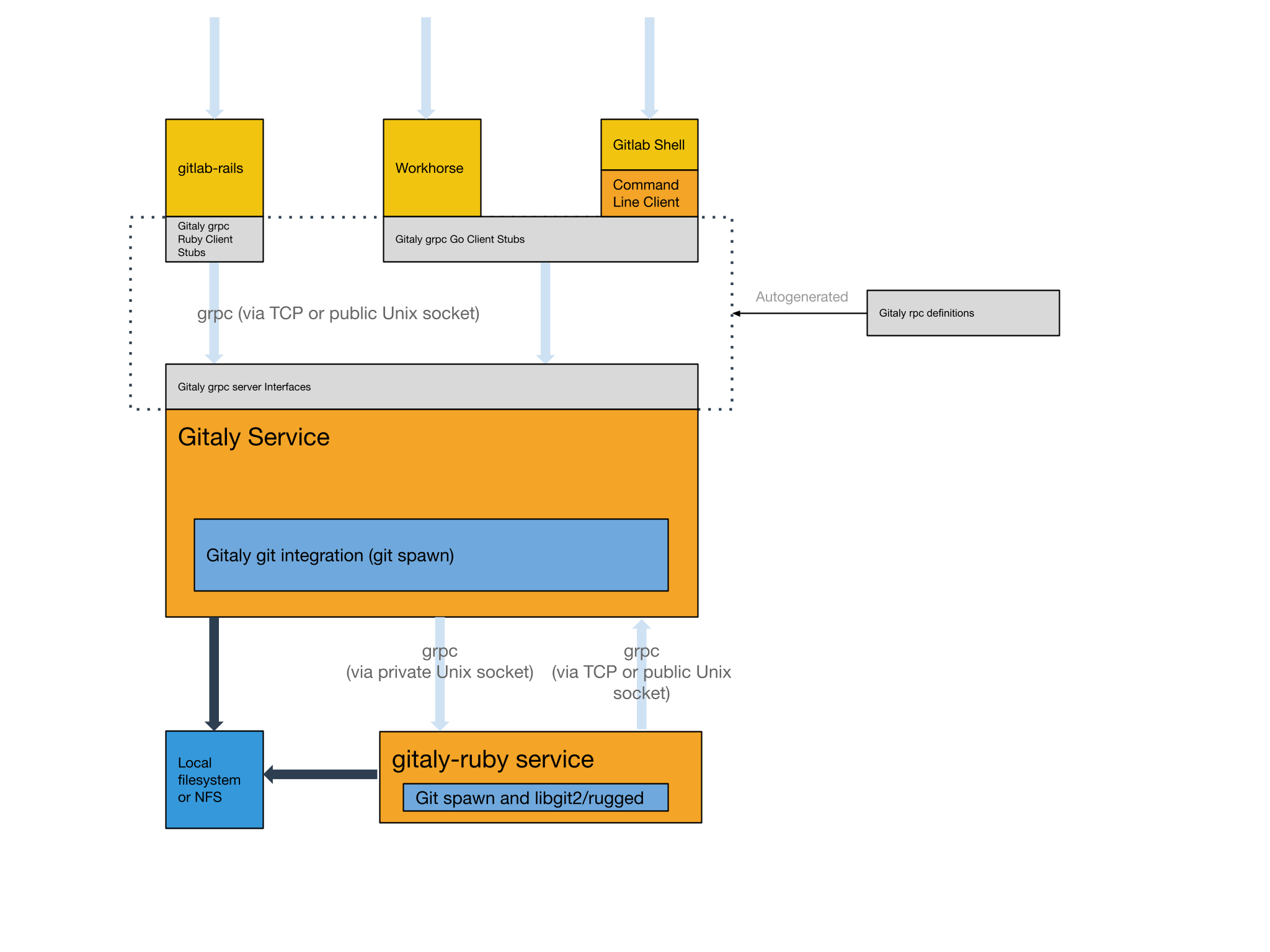
[Edit this diagram directly in Google Drawings](https://docs.google.com/drawings/d/14-5NHGvsOVaAJZl2w7pIli8iDUqed2eIbvXdff5jneo/edit)
### Gitaly clients
As of Q4 2018, the following GitLab components act as Gitaly clients:
- [gitlab-rails](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ce/blob/master/lib/gitlab/gitaly_client.rb):
the main GitLab Rails application.
- [gitlab-shell](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-shell/tree/master):
for `git clone`, `git push` etc. via SSH.
- [gitlab-workhorse](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-workhorse/blob/master/internal/gitaly/gitaly.go):
for `git clone` via HTTPS and for slow requests that serve raw Git
data.
([example](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/raw/master/README.md))
- [gitaly-ssh](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/tree/master/cmd/gitaly-ssh):
for internal Git data transfers between Gitaly servers.
- [gitaly-ruby](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/blob/master/ruby/lib/gitlab/git/gitaly_remote_repository.rb):
for RPC's that interact with more than one repository, such as
merging a branch.
The clients written in Go (gitlab-shell, gitlab-workhorse, gitaly-ssh)
use library code from the
[gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/client](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitaly/tree/master/client)
package.
## High Availability
We are working on a high-availability (HA) solution for Gitaly based on
asynchronous replication. A Gitaly server would be made highly available
by assigning one or more standby servers ("secondaries") to it, each of
which contains a full copy of all the repository data on the primary
Gitaly server.
To implement this we are building a new GitLab component called
Praefect, which is hosted alongside the rest of Gitaly in this
repository. As we currently envision it, Praefect will have four
responsibilities:
- route RPC traffic to the primary Gitaly server
- inspect RPC traffic and mark repositories as dirty if the RPC is a
"mutator"
- ensure dirty repositories have their changes replicated to the
secondary Gitaly servers
- in the event of a failure on the primary, demote it to secondary and
elect a new primary
Praefect has internal state: it needs to be able to "remember" which
repositories are in need of replication, and which Gitaly server is the
primary. [We will use Postgres to store Praefect's internal state](doc/rfcs/praefect-queue-storage.md).
As of December 2019 we are busy rolling out the Postgres integration in
Praefect. The minimum supported Postgres version is 9.6, just like the
rest of GitLab.
## Further reading
More about the project and its processes is [detailed in the docs](doc/README.md).
## Distributed Tracing
Gitaly supports distributed tracing through [LabKit](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/labkit/) using [OpenTracing APIs](https://opentracing.io).
By default, no tracing implementation is linked into the binary, but different OpenTracing providers can be linked in using [build tags](https://golang.org/pkg/go/build/#hdr-Build_Constraints)/[build constraints](https://golang.org/pkg/go/build/#hdr-Build_Constraints). This can be done by setting the `BUILD_TAGS` make variable.
For more details of the supported providers, see LabKit, but as an example, for Jaeger tracing support, include the tags: `BUILD_TAGS="tracer_static tracer_static_jaeger"`.
```shell
$ make BUILD_TAGS="tracer_static tracer_static_jaeger"
```
Once Gitaly is compiled with an opentracing provider, the tracing configuration is configured via the `GITLAB_TRACING` environment variable.
For example, to configure Jaeger, you could use the following command:
```shell
GITLAB_TRACING=opentracing://jaeger ./gitaly config.toml
```
## Continuous Profiling
Gitaly supports Continuous Profiling through [LabKit][] using [Stackdriver Profiler](https://cloud.google.com/profiler).
For more information on how to set it up, see the [LabKit monitoring docs](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/labkit/-/blob/master/monitoring/doc.go).
## Presentations
- [How to configure backpressure in Gitaly](https://youtu.be/wX9CtFdLYxE)
An overview of the knobs in the Gitaly config to set limits on incoming traffic.
There is also [written documentation](doc/backpressure.md).
- [How Gitaly fits into GitLab (Youtube)](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy) - a series of 1-hour training videos for contributors new to GitLab and Gitaly.
- [Part 1: the Gitaly client in gitlab-ce, 2019-02-21](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j0HNiKCnLTI&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
Overview of GitLab backend processes, gitlab-rails deep dive: Gitaly
config in gitlab-rails, SQL data model, overview of how Gitaly calls get
made via GitalyClient.call.
- [Part 2: Git SSH, 2019-02-28](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0kY0HPFn25o&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
What is in a gitaly-proto Repository message, legacy vs
hashed storage (repository directories), `git clone` via SSH,
gitlab-shell, `authorized_keys` and forced commands, what happens
during `git push`.
- [Part 3: Git push, 2019-03-07](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kXYycFYDzo&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
A closer look at the final stage of `git push` where the git hooks run
and the refs get updated. Interaction between the git hooks and GitLab
internal API. The Git
[object quarantine mechanism](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-receive-pack#_quarantine_environment).
Preview of Git HTTP (to be discussed next time).
- [Part 4: Git HTTP, 2019-03-14](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lM13p8lCu8A&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
Intercepting Git HTTP traffic with mitmproxy, overview of
Git HTTP clone steps, code walk in gitlab-workhorse and gitlab-ce,
investigating internal workhorse API messages used for Git HTTP.
- [Part 5: Merge Requests across Forks, 2019-03-21](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yGSuOz0XOHQ&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
Fixing a locally broken Ruby gem C
extension by recompiling, demo of how creating a MR across forks
causes new commits to suddenly appear in the fork parent repository,
deep dive into the FetchSourceBranch RPC, adding debug code to see
how address and authentication metadata is passed down to
gitaly-ruby, failed attempt to log gitaly-ssh arguments, comparison
of gitaly-ssh and gitlab-shell, a Gitaly server can end up making RPC calls to itself.
- [Part 6: Creating Git commits on behalf of Git users, 2019-03-21](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rbe0KGTLkxY&list=PL05JrBw4t0KqoFUiX42JG7BAc7pipMBAy)
Demonstrate how usually Git hooks are run by
`git-receive-pack`, but sometimes by `gitaly-ruby`. Deep dive into
UserCommitFiles: where do those hooks actually get run? A look at
UserMerge. How does Gitaly make merge commits. A look at the
implementation of the special feature where users are not allowed
push to a branch, but are allowed to merge into it.
- [Part 7: How Gitaly uses Prometheus monitoring, 2019-07-09](https://youtu.be/R6F674Nj3wI)
What is [Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/). Reconstructing a
[Grafana](https://dashboards.gitlab.com) dashboard panel
with
[PromQL](https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/querying/basics/).
Adding a new counter to Gitaly. Querying Prometheus in Gitaly
during development. Comparing latency calculation with
[ELK](https://log.gitlab.net). [GRPC Prometheus
middleware](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/go-grpc-prometheus)
in Gitaly.
- [TheConf talk on Scaling GitLab git storage with Gitaly, 2019-08-16](https://speakerdeck.com/olsfer/how-gitlab-scaled-git-access-with-a-go-service)
- [Infrastructure Team Update 2017-05-11](https://about.gitlab.com/2017/05/11/functional-group-updates/#infrastructure-team)
- [Gitaly Basics, 2017-05-01](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1cLslUbXVkniOaeJ-r3s5AYF0kQep8VeNfvs0XSGrpA0/edit#slide=id.g1c73db867d_0_0)
- [Git Paris meetup, 2017-02-22](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/19OZUalFMIDM8WujXrrIyCuVb_oVeaUzpb-UdGThOvAo/edit?usp=sharing) a high-level overview of what our plans are and where we are.
[roadmap]: https://gitlab.com/groups/gitlab-org/-/roadmap?scope=all&utf8=%E2%9C%93&label_name[]=group%3A%3Agitaly
[LabKit]: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/labkit/
|
