---
description: 'Learn how to use GitLab Pages to deploy a static website at no additional cost.'
stage: Plan
group: Knowledge
info: To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://handbook.gitlab.com/handbook/product/ux/technical-writing/#assignments
---
# GitLab Pages **(FREE ALL)**
With GitLab Pages, you can publish static websites directly from a repository
in GitLab.
- Use for any personal or business website.
- Use any Static Site Generator (SSG) or plain HTML.
- Create websites for your projects, groups, or user account.
- Host your site on your own GitLab instance or on GitLab.com for free.
- Connect your custom domains and TLS certificates.
- Attribute any license to your content.
To publish a website with Pages, you can use any static site generator,
like Gatsby, Jekyll, Hugo, Middleman, Harp, Hexo, or Brunch. You can also
publish any website written directly in plain HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Pages does not support dynamic server-side processing, for instance, as `.php` and `.asp` requires.
For more information, see
[Static vs dynamic websites](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/06/03/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-1-dynamic-x-static/).
## Getting started
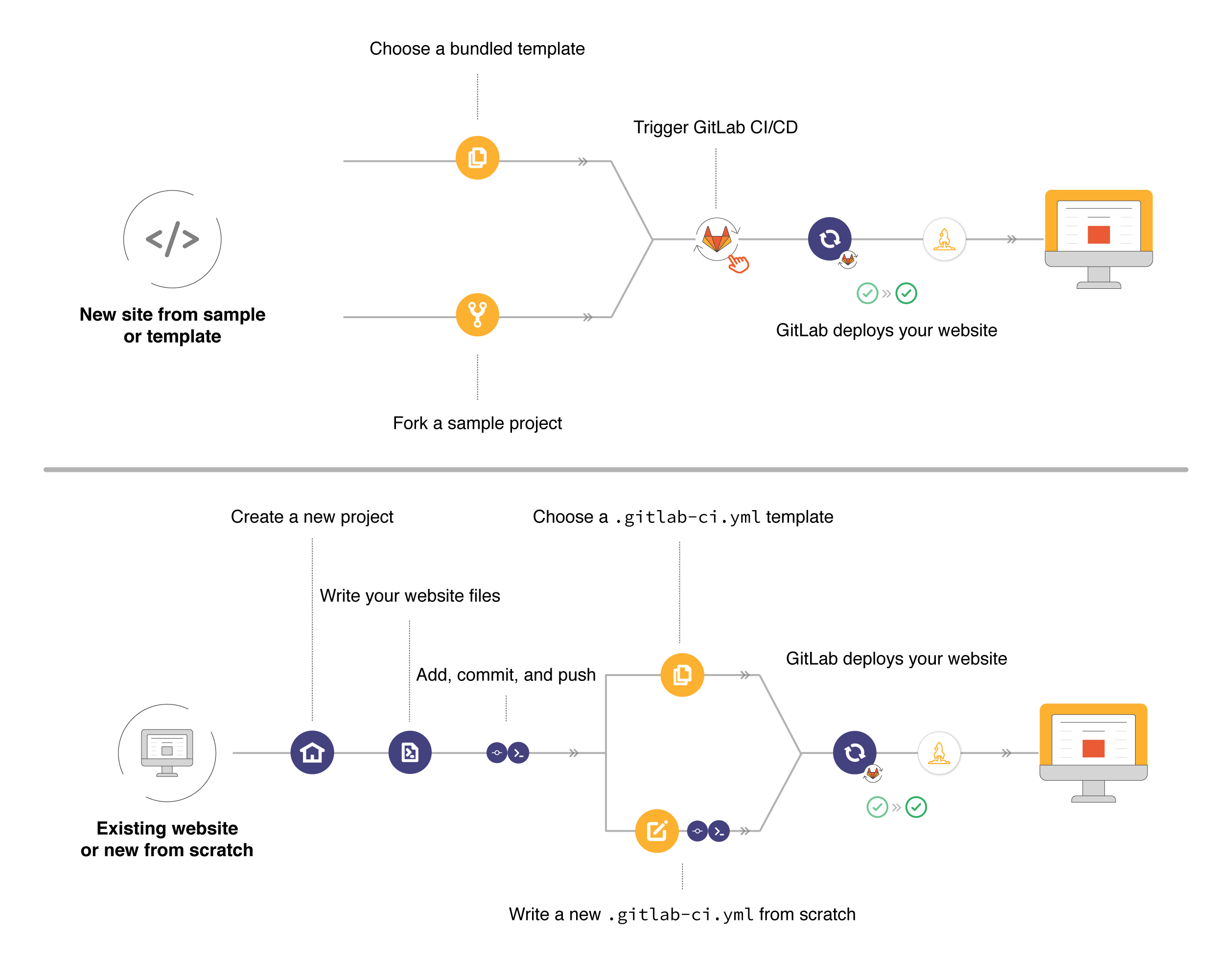
To create a GitLab Pages website:
| Document | Description |
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| [Use the GitLab UI to create a simple `.gitlab-ci.yml`](getting_started/pages_ui.md) | Add a Pages site to an existing project. Use the UI to set up a simple `.gitlab-ci.yml`. |
| [Create a `.gitlab-ci.yml` file from scratch](getting_started/pages_from_scratch.md) | Add a Pages site to an existing project. Learn how to create and configure your own CI file. |
| [Use a `.gitlab-ci.yml` template](getting_started/pages_ci_cd_template.md) | Add a Pages site to an existing project. Use a pre-populated CI template file. |
| [Fork a sample project](getting_started/pages_forked_sample_project.md) | Create a new project with Pages already configured by forking a sample project. |
| [Use a project template](getting_started/pages_new_project_template.md) | Create a new project with Pages already configured by using a template. |
To update a GitLab Pages website:
| Document | Description |
|----------|-------------|
| [GitLab Pages domain names, URLs, and base URLs](getting_started_part_one.md) | Learn about GitLab Pages default domains. |
| [Explore GitLab Pages](introduction.md) | Requirements, technical aspects, specific GitLab CI/CD configuration options, Access Control, custom 404 pages, limitations, and FAQ. |
| [Custom domains and SSL/TLS Certificates](custom_domains_ssl_tls_certification/index.md) | Custom domains and subdomains, DNS records, and SSL/TLS certificates. |
| [Let's Encrypt integration](custom_domains_ssl_tls_certification/lets_encrypt_integration.md) | Secure your Pages sites with Let's Encrypt certificates, which are automatically obtained and renewed by GitLab. |
| [Redirects](redirects.md) | Set up HTTP redirects to forward one page to another. |
For more information, see:
| Document | Description |
|----------|-------------|
| [Static vs dynamic websites](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/06/03/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-1-dynamic-x-static/) | Static versus dynamic site overview. |
| [Modern static site generators](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/06/10/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-2/) | SSG overview. |
| [Build any SSG site with GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/06/17/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-3-examples-ci/) | Use SSGs for GitLab Pages. |
## How it works
To use GitLab Pages, you must create a project in GitLab to upload your website's
files to. These projects can be either public, internal, or private.
GitLab always deploys your website from a specific folder called `public` in your
repository. When you create a new project in GitLab, a [repository](../repository/index.md)
becomes available automatically.
To deploy your site, GitLab uses its built-in tool called [GitLab CI/CD](../../../ci/index.md)
to build your site and publish it to the GitLab Pages server. The sequence of
scripts that GitLab CI/CD runs to accomplish this task is created from a file named
`.gitlab-ci.yml`, which you can [create and modify](getting_started/pages_from_scratch.md).
A specific `job` called `pages` in the configuration file makes GitLab aware that you're deploying a
GitLab Pages website.
You can either use the GitLab [default domain for GitLab Pages websites](getting_started_part_one.md#gitlab-pages-default-domain-names),
`*.gitlab.io`, or your own domain (`example.com`). In that case, you
must be an administrator in your domain's registrar (or control panel) to set it up with Pages.
The following diagrams show the workflows you might follow to get started with Pages.
 ## Access to your Pages site
If you're using GitLab Pages default domain (`.gitlab.io`), your website is
automatically secure and available under HTTPS. If you're using your own custom
domain, you can optionally secure it with SSL/TLS certificates.
If you're using GitLab.com, your website is publicly available to the internet.
To restrict access to your website, enable [GitLab Pages Access Control](pages_access_control.md).
If you're using a self-managed instance, your websites are published on your
own server, according to the [Pages settings](../../../administration/pages/index.md)
chosen by your sysadmin, who can make them public or internal.
## Pages examples
These GitLab Pages website examples can teach you advanced techniques to use
and adapt for your own needs:
- [Posting to your GitLab Pages blog from iOS](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/08/19/posting-to-your-gitlab-pages-blog-from-ios/).
- [GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel, or build a custom pipeline](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2020/12/10/basics-of-gitlab-ci-updated/).
- [GitLab CI: Deployment & environments](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2021/02/05/ci-deployment-and-environments/).
- [Building a new GitLab docs site with Nanoc, GitLab CI, and GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/12/07/building-a-new-gitlab-docs-site-with-nanoc-gitlab-ci-and-gitlab-pages/).
- [Publish code coverage reports with GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/11/03/publish-code-coverage-report-with-gitlab-pages/).
## Administer GitLab Pages for self-managed instances
If you are running a self-managed instance of GitLab,
[follow the administration steps](../../../administration/pages/index.md) to configure Pages.
Watch a [video tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dD8c7WNcc6s) about how to get started with GitLab Pages administration.
### Configure GitLab Pages in a Helm Chart (Kubernetes) instance
To configure GitLab Pages on instances deployed via Helm chart (Kubernetes), use either:
- [The `gitlab-pages` subchart](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/charts/gitlab/gitlab-pages/).
- [An external GitLab Pages instance](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/advanced/external-gitlab-pages/).
## Security for GitLab Pages
### Namespaces that contain `.`
If your username is `example`, your GitLab Pages website is located at `example.gitlab.io`.
GitLab allows usernames to contain a `.`, so a user named `bar.example` could create
a GitLab Pages website `bar.example.gitlab.io` that effectively is a subdomain of your
`example.gitlab.io` website. Be careful if you use JavaScript to set cookies for your website.
The safe way to manually set cookies with JavaScript is to not specify the `domain` at all:
```javascript
// Safe: This cookie is only visible to example.gitlab.io
document.cookie = "key=value";
// Unsafe: This cookie is visible to example.gitlab.io and its subdomains,
// regardless of the presence of the leading dot.
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=.example.gitlab.io";
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=example.gitlab.io";
```
This issue doesn't affect users with a custom domain, or users who don't set any
cookies manually with JavaScript.
### Shared cookies
By default, every project in a group shares the same domain, for example, `group.gitlab.io`. This means that cookies are also shared for all projects in a group.
To ensure each project uses different cookies, enable the Pages [unique domains](introduction.md#enable-unique-domains) feature for your project.
## Create multiple deployments **(PREMIUM ALL EXPERIMENT)**
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/merge_requests/129534) in GitLab 16.7 as an [Experiment](../../../policy/experiment-beta-support.md) [with a flag](../../feature_flags.md) named `pages_multiple_versions_setting`, disabled by default.
FLAG:
On self-managed GitLab, by default this feature is not available. To make it available,
an administrator can [enable the feature flag](../../../administration/feature_flags.md) named
`pages_multiple_versions_setting`. On GitLab.com, this feature is not available. This feature is not ready for production use.
Use the [`pages.path_prefix`](../../../ci/yaml/index.md#pagespagespath_prefix) CI/CD option to configure a prefix for the GitLab Pages URL. A prefix allows you
to differentiate between multiple GitLab Pages deployments.
Multiple GitLab Pages deployments (pages created with a `path_prefix`) count toward your [storage](../../../user/usage_quotas.md) usage.
### Enable multiple deployments
To enable multiple GitLab Pages deployments:
1. On the left sidebar, select **Search or go to** and find your project.
1. Select **Deploy > Pages**.
1. Select **Use multiple deployments**.
### Path clash
`pages.path_prefix` can take dynamic values from [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md)
that can create pages deployments which could clash with existing paths in your site.
For example, given an existing GitLab Pages site with the following paths:
```plaintext
/index.html
/documents/index.html
```
If a `pages.path_prefix` is `documents`, that version will override the existing path.
In other words, `https://namespace.gitlab.io/project/documents/index.html` will point to the
`/index.html` on the `documents` deployment of the site, instead of `documents/index.html` of the
`main` deployment of the site.
Mixing [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with other strings can reduce the path clash
possibility. For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # No prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH # Run on default branch (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # Run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # Prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # Conditionally change the prefix for Merge Requests
when: manual # Run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # Prefix with the mr, like `mr123`
```
Some other examples of mixing [variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with strings for dynamic prefixes:
- `pages.path_prefix: '__$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG'`: Branch or tag name prefixed with `__`, like `__branch-name`.
- `pages.path_prefix: '-${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}-'`: Merge request number prefixed and suffixed with `-`, like `-123-`.
### Use multiple deployments to create pages environments
You can use multiple GitLap Pages deployments to create a new [environment](../../../ci/environments/index.md).
For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # no prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
environment:
name: "Pages ${PAGES_PREFIX}"
url: "${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # ensure to run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # conditionally change the prefix on Merge Requests
when: manual # run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # prefix with the mr, like `mr123`
```
With this configuration, users will have the access to each GitLab Pages deployment through the UI.
When using [environments](../../../ci/environments/index.md) for pages, all pages environments are
listed on the project environment list.
## Access to your Pages site
If you're using GitLab Pages default domain (`.gitlab.io`), your website is
automatically secure and available under HTTPS. If you're using your own custom
domain, you can optionally secure it with SSL/TLS certificates.
If you're using GitLab.com, your website is publicly available to the internet.
To restrict access to your website, enable [GitLab Pages Access Control](pages_access_control.md).
If you're using a self-managed instance, your websites are published on your
own server, according to the [Pages settings](../../../administration/pages/index.md)
chosen by your sysadmin, who can make them public or internal.
## Pages examples
These GitLab Pages website examples can teach you advanced techniques to use
and adapt for your own needs:
- [Posting to your GitLab Pages blog from iOS](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/08/19/posting-to-your-gitlab-pages-blog-from-ios/).
- [GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel, or build a custom pipeline](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2020/12/10/basics-of-gitlab-ci-updated/).
- [GitLab CI: Deployment & environments](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2021/02/05/ci-deployment-and-environments/).
- [Building a new GitLab docs site with Nanoc, GitLab CI, and GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/12/07/building-a-new-gitlab-docs-site-with-nanoc-gitlab-ci-and-gitlab-pages/).
- [Publish code coverage reports with GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/11/03/publish-code-coverage-report-with-gitlab-pages/).
## Administer GitLab Pages for self-managed instances
If you are running a self-managed instance of GitLab,
[follow the administration steps](../../../administration/pages/index.md) to configure Pages.
Watch a [video tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dD8c7WNcc6s) about how to get started with GitLab Pages administration.
### Configure GitLab Pages in a Helm Chart (Kubernetes) instance
To configure GitLab Pages on instances deployed via Helm chart (Kubernetes), use either:
- [The `gitlab-pages` subchart](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/charts/gitlab/gitlab-pages/).
- [An external GitLab Pages instance](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/advanced/external-gitlab-pages/).
## Security for GitLab Pages
### Namespaces that contain `.`
If your username is `example`, your GitLab Pages website is located at `example.gitlab.io`.
GitLab allows usernames to contain a `.`, so a user named `bar.example` could create
a GitLab Pages website `bar.example.gitlab.io` that effectively is a subdomain of your
`example.gitlab.io` website. Be careful if you use JavaScript to set cookies for your website.
The safe way to manually set cookies with JavaScript is to not specify the `domain` at all:
```javascript
// Safe: This cookie is only visible to example.gitlab.io
document.cookie = "key=value";
// Unsafe: This cookie is visible to example.gitlab.io and its subdomains,
// regardless of the presence of the leading dot.
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=.example.gitlab.io";
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=example.gitlab.io";
```
This issue doesn't affect users with a custom domain, or users who don't set any
cookies manually with JavaScript.
### Shared cookies
By default, every project in a group shares the same domain, for example, `group.gitlab.io`. This means that cookies are also shared for all projects in a group.
To ensure each project uses different cookies, enable the Pages [unique domains](introduction.md#enable-unique-domains) feature for your project.
## Create multiple deployments **(PREMIUM ALL EXPERIMENT)**
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/merge_requests/129534) in GitLab 16.7 as an [Experiment](../../../policy/experiment-beta-support.md) [with a flag](../../feature_flags.md) named `pages_multiple_versions_setting`, disabled by default.
FLAG:
On self-managed GitLab, by default this feature is not available. To make it available,
an administrator can [enable the feature flag](../../../administration/feature_flags.md) named
`pages_multiple_versions_setting`. On GitLab.com, this feature is not available. This feature is not ready for production use.
Use the [`pages.path_prefix`](../../../ci/yaml/index.md#pagespagespath_prefix) CI/CD option to configure a prefix for the GitLab Pages URL. A prefix allows you
to differentiate between multiple GitLab Pages deployments.
Multiple GitLab Pages deployments (pages created with a `path_prefix`) count toward your [storage](../../../user/usage_quotas.md) usage.
### Enable multiple deployments
To enable multiple GitLab Pages deployments:
1. On the left sidebar, select **Search or go to** and find your project.
1. Select **Deploy > Pages**.
1. Select **Use multiple deployments**.
### Path clash
`pages.path_prefix` can take dynamic values from [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md)
that can create pages deployments which could clash with existing paths in your site.
For example, given an existing GitLab Pages site with the following paths:
```plaintext
/index.html
/documents/index.html
```
If a `pages.path_prefix` is `documents`, that version will override the existing path.
In other words, `https://namespace.gitlab.io/project/documents/index.html` will point to the
`/index.html` on the `documents` deployment of the site, instead of `documents/index.html` of the
`main` deployment of the site.
Mixing [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with other strings can reduce the path clash
possibility. For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # No prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH # Run on default branch (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # Run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # Prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # Conditionally change the prefix for Merge Requests
when: manual # Run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # Prefix with the mr, like `mr123`
```
Some other examples of mixing [variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with strings for dynamic prefixes:
- `pages.path_prefix: '__$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG'`: Branch or tag name prefixed with `__`, like `__branch-name`.
- `pages.path_prefix: '-${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}-'`: Merge request number prefixed and suffixed with `-`, like `-123-`.
### Use multiple deployments to create pages environments
You can use multiple GitLap Pages deployments to create a new [environment](../../../ci/environments/index.md).
For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # no prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
environment:
name: "Pages ${PAGES_PREFIX}"
url: "${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # ensure to run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # conditionally change the prefix on Merge Requests
when: manual # run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # prefix with the mr, like `mr123`
```
With this configuration, users will have the access to each GitLab Pages deployment through the UI.
When using [environments](../../../ci/environments/index.md) for pages, all pages environments are
listed on the project environment list.

 ## Access to your Pages site
If you're using GitLab Pages default domain (`.gitlab.io`), your website is
automatically secure and available under HTTPS. If you're using your own custom
domain, you can optionally secure it with SSL/TLS certificates.
If you're using GitLab.com, your website is publicly available to the internet.
To restrict access to your website, enable [GitLab Pages Access Control](pages_access_control.md).
If you're using a self-managed instance, your websites are published on your
own server, according to the [Pages settings](../../../administration/pages/index.md)
chosen by your sysadmin, who can make them public or internal.
## Pages examples
These GitLab Pages website examples can teach you advanced techniques to use
and adapt for your own needs:
- [Posting to your GitLab Pages blog from iOS](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/08/19/posting-to-your-gitlab-pages-blog-from-ios/).
- [GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel, or build a custom pipeline](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2020/12/10/basics-of-gitlab-ci-updated/).
- [GitLab CI: Deployment & environments](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2021/02/05/ci-deployment-and-environments/).
- [Building a new GitLab docs site with Nanoc, GitLab CI, and GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/12/07/building-a-new-gitlab-docs-site-with-nanoc-gitlab-ci-and-gitlab-pages/).
- [Publish code coverage reports with GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/11/03/publish-code-coverage-report-with-gitlab-pages/).
## Administer GitLab Pages for self-managed instances
If you are running a self-managed instance of GitLab,
[follow the administration steps](../../../administration/pages/index.md) to configure Pages.
Watch a [video tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dD8c7WNcc6s) about how to get started with GitLab Pages administration.
### Configure GitLab Pages in a Helm Chart (Kubernetes) instance
To configure GitLab Pages on instances deployed via Helm chart (Kubernetes), use either:
- [The `gitlab-pages` subchart](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/charts/gitlab/gitlab-pages/).
- [An external GitLab Pages instance](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/advanced/external-gitlab-pages/).
## Security for GitLab Pages
### Namespaces that contain `.`
If your username is `example`, your GitLab Pages website is located at `example.gitlab.io`.
GitLab allows usernames to contain a `.`, so a user named `bar.example` could create
a GitLab Pages website `bar.example.gitlab.io` that effectively is a subdomain of your
`example.gitlab.io` website. Be careful if you use JavaScript to set cookies for your website.
The safe way to manually set cookies with JavaScript is to not specify the `domain` at all:
```javascript
// Safe: This cookie is only visible to example.gitlab.io
document.cookie = "key=value";
// Unsafe: This cookie is visible to example.gitlab.io and its subdomains,
// regardless of the presence of the leading dot.
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=.example.gitlab.io";
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=example.gitlab.io";
```
This issue doesn't affect users with a custom domain, or users who don't set any
cookies manually with JavaScript.
### Shared cookies
By default, every project in a group shares the same domain, for example, `group.gitlab.io`. This means that cookies are also shared for all projects in a group.
To ensure each project uses different cookies, enable the Pages [unique domains](introduction.md#enable-unique-domains) feature for your project.
## Create multiple deployments **(PREMIUM ALL EXPERIMENT)**
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/merge_requests/129534) in GitLab 16.7 as an [Experiment](../../../policy/experiment-beta-support.md) [with a flag](../../feature_flags.md) named `pages_multiple_versions_setting`, disabled by default.
FLAG:
On self-managed GitLab, by default this feature is not available. To make it available,
an administrator can [enable the feature flag](../../../administration/feature_flags.md) named
`pages_multiple_versions_setting`. On GitLab.com, this feature is not available. This feature is not ready for production use.
Use the [`pages.path_prefix`](../../../ci/yaml/index.md#pagespagespath_prefix) CI/CD option to configure a prefix for the GitLab Pages URL. A prefix allows you
to differentiate between multiple GitLab Pages deployments.
Multiple GitLab Pages deployments (pages created with a `path_prefix`) count toward your [storage](../../../user/usage_quotas.md) usage.
### Enable multiple deployments
To enable multiple GitLab Pages deployments:
1. On the left sidebar, select **Search or go to** and find your project.
1. Select **Deploy > Pages**.
1. Select **Use multiple deployments**.
### Path clash
`pages.path_prefix` can take dynamic values from [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md)
that can create pages deployments which could clash with existing paths in your site.
For example, given an existing GitLab Pages site with the following paths:
```plaintext
/index.html
/documents/index.html
```
If a `pages.path_prefix` is `documents`, that version will override the existing path.
In other words, `https://namespace.gitlab.io/project/documents/index.html` will point to the
`/index.html` on the `documents` deployment of the site, instead of `documents/index.html` of the
`main` deployment of the site.
Mixing [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with other strings can reduce the path clash
possibility. For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # No prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH # Run on default branch (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # Run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # Prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # Conditionally change the prefix for Merge Requests
when: manual # Run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # Prefix with the mr
## Access to your Pages site
If you're using GitLab Pages default domain (`.gitlab.io`), your website is
automatically secure and available under HTTPS. If you're using your own custom
domain, you can optionally secure it with SSL/TLS certificates.
If you're using GitLab.com, your website is publicly available to the internet.
To restrict access to your website, enable [GitLab Pages Access Control](pages_access_control.md).
If you're using a self-managed instance, your websites are published on your
own server, according to the [Pages settings](../../../administration/pages/index.md)
chosen by your sysadmin, who can make them public or internal.
## Pages examples
These GitLab Pages website examples can teach you advanced techniques to use
and adapt for your own needs:
- [Posting to your GitLab Pages blog from iOS](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/08/19/posting-to-your-gitlab-pages-blog-from-ios/).
- [GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel, or build a custom pipeline](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2020/12/10/basics-of-gitlab-ci-updated/).
- [GitLab CI: Deployment & environments](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2021/02/05/ci-deployment-and-environments/).
- [Building a new GitLab docs site with Nanoc, GitLab CI, and GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/12/07/building-a-new-gitlab-docs-site-with-nanoc-gitlab-ci-and-gitlab-pages/).
- [Publish code coverage reports with GitLab Pages](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/11/03/publish-code-coverage-report-with-gitlab-pages/).
## Administer GitLab Pages for self-managed instances
If you are running a self-managed instance of GitLab,
[follow the administration steps](../../../administration/pages/index.md) to configure Pages.
Watch a [video tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dD8c7WNcc6s) about how to get started with GitLab Pages administration.
### Configure GitLab Pages in a Helm Chart (Kubernetes) instance
To configure GitLab Pages on instances deployed via Helm chart (Kubernetes), use either:
- [The `gitlab-pages` subchart](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/charts/gitlab/gitlab-pages/).
- [An external GitLab Pages instance](https://docs.gitlab.com/charts/advanced/external-gitlab-pages/).
## Security for GitLab Pages
### Namespaces that contain `.`
If your username is `example`, your GitLab Pages website is located at `example.gitlab.io`.
GitLab allows usernames to contain a `.`, so a user named `bar.example` could create
a GitLab Pages website `bar.example.gitlab.io` that effectively is a subdomain of your
`example.gitlab.io` website. Be careful if you use JavaScript to set cookies for your website.
The safe way to manually set cookies with JavaScript is to not specify the `domain` at all:
```javascript
// Safe: This cookie is only visible to example.gitlab.io
document.cookie = "key=value";
// Unsafe: This cookie is visible to example.gitlab.io and its subdomains,
// regardless of the presence of the leading dot.
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=.example.gitlab.io";
document.cookie = "key=value;domain=example.gitlab.io";
```
This issue doesn't affect users with a custom domain, or users who don't set any
cookies manually with JavaScript.
### Shared cookies
By default, every project in a group shares the same domain, for example, `group.gitlab.io`. This means that cookies are also shared for all projects in a group.
To ensure each project uses different cookies, enable the Pages [unique domains](introduction.md#enable-unique-domains) feature for your project.
## Create multiple deployments **(PREMIUM ALL EXPERIMENT)**
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/merge_requests/129534) in GitLab 16.7 as an [Experiment](../../../policy/experiment-beta-support.md) [with a flag](../../feature_flags.md) named `pages_multiple_versions_setting`, disabled by default.
FLAG:
On self-managed GitLab, by default this feature is not available. To make it available,
an administrator can [enable the feature flag](../../../administration/feature_flags.md) named
`pages_multiple_versions_setting`. On GitLab.com, this feature is not available. This feature is not ready for production use.
Use the [`pages.path_prefix`](../../../ci/yaml/index.md#pagespagespath_prefix) CI/CD option to configure a prefix for the GitLab Pages URL. A prefix allows you
to differentiate between multiple GitLab Pages deployments.
Multiple GitLab Pages deployments (pages created with a `path_prefix`) count toward your [storage](../../../user/usage_quotas.md) usage.
### Enable multiple deployments
To enable multiple GitLab Pages deployments:
1. On the left sidebar, select **Search or go to** and find your project.
1. Select **Deploy > Pages**.
1. Select **Use multiple deployments**.
### Path clash
`pages.path_prefix` can take dynamic values from [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md)
that can create pages deployments which could clash with existing paths in your site.
For example, given an existing GitLab Pages site with the following paths:
```plaintext
/index.html
/documents/index.html
```
If a `pages.path_prefix` is `documents`, that version will override the existing path.
In other words, `https://namespace.gitlab.io/project/documents/index.html` will point to the
`/index.html` on the `documents` deployment of the site, instead of `documents/index.html` of the
`main` deployment of the site.
Mixing [CI/CD variables](../../../ci/variables/index.md) with other strings can reduce the path clash
possibility. For example:
```yaml
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Pages accessible through ${CI_PAGES_URL}/${PAGES_PREFIX}"
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: "" # No prefix by default (master)
pages:
path_prefix: "$PAGES_PREFIX"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH # Run on default branch (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "staging" # Run on master (with default PAGES_PREFIX)
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: '_stg' # Prefix with _stg for the staging branch
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" # Conditionally change the prefix for Merge Requests
when: manual # Run pages manually on Merge Requests
variables:
PAGES_PREFIX: 'mr$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID' # Prefix with the mr